Resources
A Resource in the context of the Witboost Computational Governance (WCG) refers to any object that can be described by metadata. Those resources, if managed by Witboost, can be evaluated by WCG's Governance Entities so that you can control their compliance within your data governance strategy during their whole lifecycle.
Resources originate from various aspects of the software and data development processes and can encompass a wide range of objects such as datasets, build files, configurations, and more. In the Witboost Computational Governance, they are implicitly described by these characteristics:
- ID: a unique name within the platform to identify each of them
- Version: a version that allows you to distinguish between different iterations of the same resource
- Descriptor: Metadata about the resource, usually, but not limited to, a YAML file.
- Resource Type: As explained in the Overview section, It describes how the descriptor looks
like, so that
Governance Entities can indicate to be
compatible with this type of resource. An example Resource Type is the Data Product, where a descriptor is known to be
composed by specific fields e.g. the
componentsfield.
Resources Perimeter
A Governance Entity most of the times does not apply to any resources. It is instead scoped to a specific set of resources that fall within the so called perimeter.
The perimeter is defined by the combination of:
- Resource Type: the type of resources the Governance Entity applies to
- Environment: the environment the Governance Entity applies to
- Selectors: a set of key-value pairs that further filter the resources the Governance Entity applies to
- Infrastructure Template ID and Use Case Template ID: further filters that can be used to restrict the resources the Governance Entity applies to
Resources Perimeters are computed by the Witboost Computational Governance whenever you are testing a Governance Entity or when a Governance Entity is set be initiated by WCG, e.g. Runtime Policies or Metrics.
Instead, WCG does not compute the perimeter whenever you are evaluating a resource against a Policy or Metric with Deployment timing, because in that case it is your evaluation request that comes with the resource attached. In such case, WCG only checks if the resource you are evaluating is compatible with the Governance Entity's perimeter.
Perimeter Resolvers
A Perimeter Resolver is a Witboost Extension Point that implements the Perimeter Resolver API (see Witboost Extension Points API).
The Computational Governance uses Perimeter Resolvers to compute a Governance Entity's resource perimeter during an evaluation.
This happens in three cases:
- During a Governance Entity test: used to assess if the Policy or Metric performs all needed checks and how it is applied to resources that are already deployed within your organization. The list of resources being evaluated during a test is the perimeter of resources of the Governance Entity being tested.
- During a Runtime Policy or Metric evaluation: used to periodically check if all resources within the Governance Entity's perimeter are compliant with the defined policies and metrics.
- During the evaluation of a Policy or Metric with Previous vs Current preprocessing mode: used to retrieve the current version of the resource being evaluated, in order to compare it with the new version being deployed.
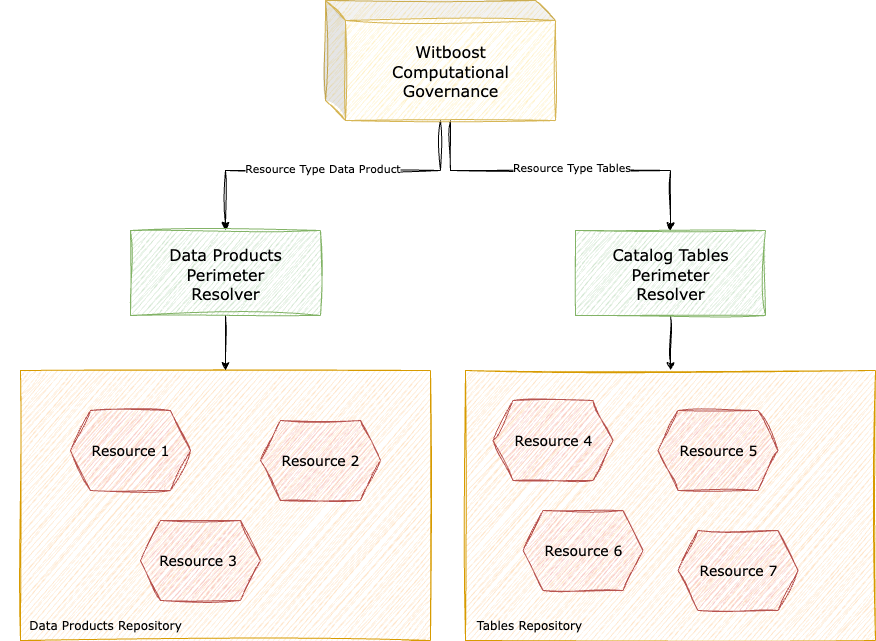
A diagram representation of Perimeter Resolvers
Perimeter Resolvers is a powerful abstraction for the Computational Governance because it allows you to make any resource evaluable by Policies or Metrics defined in a central platform like Witboost.
Extending Resource Types
Witboost Computational Governance is capable of working with different types of resources. Once you implemented a Perimeter Resolver capable of retrieving resources of a new type, you can configure WCG to be aware of this new Resource Type, you can either:
- Register the new Resource Type through the WCG API at
POST /v1/computational-governance/resource-types - Register a new system type in the Practice Shaper and attach there the configuration of the new Resource Type and Perimeter Resolver
Alternatively, it's also possible to statically configure resource types by configuration (refer to the Witboost Computational Governance Configuration section of the documentation).
If you are working with the full Witboost platform, the recommended way to register new Resource Types is through the Practice Shaper, as it will ensure that the configuration is consistent across all Witboost modules.